“TF-A overview”的版本间的差异
| (未显示同一用户的2个中间版本) | |||
| 第1行: | 第1行: | ||
== Trusted Firmware-A == | == Trusted Firmware-A == | ||
| − | [[File: STM32MPU Embedded Software architecture overview.png|link=STM32MPU Embedded Software architecture overview|thumb| | + | [[File: STM32MPU Embedded Software architecture overview.png|link=STM32MPU Embedded Software architecture overview|thumb|缩小到STM32MPU嵌入式软件]] |
Trusted Firmware-A是Arm提供的安全世界软件的参考实现。<sup>®</sup>. 它最初是为Armv8-A平台设计的,并已由意法半导体(STMicroelectronics)改编为用于Armv7-A平台。 Arm正在转让Trusted Firmware项目,该项目将由Linaro作为开源项目进行管理。<ref>https://www.trustedfirmware.org/</ref> | Trusted Firmware-A是Arm提供的安全世界软件的参考实现。<sup>®</sup>. 它最初是为Armv8-A平台设计的,并已由意法半导体(STMicroelectronics)改编为用于Armv7-A平台。 Arm正在转让Trusted Firmware项目,该项目将由Linaro作为开源项目进行管理。<ref>https://www.trustedfirmware.org/</ref> | ||
| 第18行: | 第18行: | ||
== Architecture == | == Architecture == | ||
| − | + | TF-A的全局体系结构在Trusted Firmware-A设计文档中进行了说明 <ref>{{CodeSource | TF-A | docs/firmware-design.rst}}</ref>。 | |
| − | TF- | + | TF-A分为几个二进制文件,每个都有专门的主要角色。 对于32位Arm处理器(AArch32),它分为四个步骤(按执行顺序): |
| − | * | + | * 引导加载程序第1阶段(BL1)应用处理器受信任的ROM |
| − | * | + | * 引导加载程序第2阶段(BL2)受信任的引导固件 |
| − | * | + | * 引导加载程序阶段3-2(BL32)运行时软件 |
| − | * | + | * 引导加载程序阶段3-3(BL33)不可信固件 |
| − | + | BL1,BL2和BL32是TF-A的一部分。 | |
| − | + | BL1现在是可选的,并且可以通过启用编译标志BL2_AT_EL3来删除。 然后将其删除以用于STM32MP1,因为所有BL1任务均由 [[:Category:ROM code|ROM code]]或BL2完成。 | |
| + | BL33在TF-A之外。 这是TF-A加载的第一个非安全代码。 在引导过程中,这是二级引导加载程序(SSBL)。 对于STM32 MPU平台,默认情况下,SSBL为[[U-Boot overview|U-Boot]]。 | ||
| − | + | TF-A可以使用[[STM32MP15_device_tree#Device tree structure for Linux, U-Boot and TF-A|device tree]]管理其配置,因为STM32MP1就是这种情况。它是Linux内核的简化版本,仅在引导过程中使用设备。可以使用[[STM32CubeMX]]进行配置。 | |
| − | + | 在意法半导体(STMicroelectronics)的实现中,将2个二进制文件BL2和BL32以及设备树放到一个二进制文件中,然后通过ROM代码立即将其加载到SYSRAM中。 | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[File:Boot_ATF.png|center|link=]] | [[File:Boot_ATF.png|center|link=]] | ||
| 第40行: | 第39行: | ||
[[File:Boot_ATF_legend.png|center|link=]] | [[File:Boot_ATF_legend.png|center|link=]] | ||
| − | TF- | + | TF-A加载步骤: |
| − | # | + | # ROM代码加载TF-A二进制文件并调用BL2 |
| − | # | + | # BL2准备BL32 |
| − | # | + | # BL2加载BL33 |
| − | # | + | # BL2呼叫BL32 |
| − | # | + | # BL32呼叫BL33 |
== Boot loader stages == | == Boot loader stages == | ||
=== BL1 === | === BL1 === | ||
| − | + | BL1是第一个执行阶段,设计为充当ROM代码;它在内部RAM中加载和执行。 | |
| − | + | 不适用于STM32MP1。由于STM32MP1具有其专有的 [[:Category:ROM code|ROM code]],因此可以删除此部分,然后BL2是第一个要执行的TF-A二进制文件。 | |
=== BL2 === | === BL2 === | ||
| − | + | BL2(受信任的引导固件)负责加载下一阶段的映像(安全和不安全)。 | |
| − | + | 为了实现此作用,BL2必须初始化所有必需的外围设备。 | |
| − | + | 它必须初始化安全组件。<br> | |
| − | + | 对于STM32MP15,这些安全外围设备为: | |
| − | * | + | * 引导和安全性以及OTP控制 ([[BSEC internal peripheral]]) |
| − | * | + | * 扩展的TrustZone保护控制器([[ETZPC internal peripheral]]) |
| − | * | + | * DDR的TrustZone地址空间控制器([[TZC internal peripheral]]) |
| − | + | BL2还负责初始化DDR和时钟树。 | |
| − | + | 引导外围设备必须初始化。<br> | |
| − | + | 在STM32MP15上,它可以是以下之一: | |
| − | * | + | * 通过[[SDMMC internal peripheral]]的SD卡 |
| − | * | + | * 通过[[SDMMC internal peripheral]]的eMMC |
| − | * | + | * 通过[[FMC internal peripheral]]进行NAND |
| − | * | + | * NOR通过[[QUADSPI internal peripheral]] |
| − | + | 在使用中闪烁时使用USB ([[OTG internal peripheral]]) 或 UART([[USART internal peripheral]]) , 有关更多详细信息,请参见[[STM32CubeProgrammer]]。 | |
| − | + | BL2还集成了图像验证和身份验证。通过调用[[STM32MP15 ROM code overview|BootROM]]验证服务来实现身份验证。 | |
| − | + | 在执行结束时,在加载BL32和下一个引导阶段(BL33)之后,BL2跳至BL32。 | |
=== BL32 === | === BL32 === | ||
| − | + | BL32提供运行时安全服务。在TF-A中,BL32的默认实现是SP_min解决方案。 | |
| − | + | 在TF-A功能列表 <ref name=readme/> 中将其描述为: | |
| − | + | “最小的AArch32安全有效载荷(SP_MIN),用于演示PSCI <ref name=psci/> 库与AArch32 EL3运行时软件的集成。” | |
| − | + | 可以用可信任的OS或可信任的环境执行(TEE)代替此最小实现,例如[[OP-TEE overview|OP-TEE]]。 | |
| − | |||
| − | + | STMicroelectronics针对STM32MP1支持两种解决方案(SP_min或OP-TEE)。 | |
| − | + | BL32充当安全监视器,从而为非安全OS提供安全服务。 这些服务由具有安全监视器调用的非安全软件调用 <ref name=smc/>. | |
| − | + | 此代码负责标准服务呼叫,例如PSCI<ref name=psci/>.<br/> | |
| + | |||
| + | 它还提供 STMicroelectronics 专用服务, 以访问安全外围设备。 在STM32MP1上,这些服务用于访问 [[RCC internal peripheral]], [[PWR internal peripheral]], [[RTC internal peripheral]] 或 [[BSEC internal peripheral]]. | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
2020年11月2日 (一) 10:48的最新版本
Trusted Firmware-A
Trusted Firmware-A是Arm提供的安全世界软件的参考实现。®. 它最初是为Armv8-A平台设计的,并已由意法半导体(STMicroelectronics)改编为用于Armv7-A平台。 Arm正在转让Trusted Firmware项目,该项目将由Linaro作为开源项目进行管理。[1]
当使用STM32 MPU平台时,它用作STM32 MPU平台上的第一阶段引导加载程序(FSBL)。 trusted boot chain.
该代码在BSD-3-Clause许可下是开源的,可以在github上找到 [2], 包括有关Trusted Firmware-A安装的最新文档 [3].
Trusted Firmware-A还使用各种Arm接口标准实施安全的监视器:
Trusted Firmware-A 通常缩写为 TF-A.
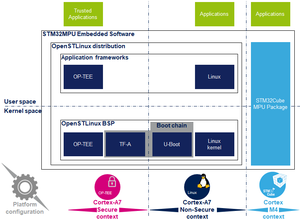
Architecture
TF-A的全局体系结构在Trusted Firmware-A设计文档中进行了说明 [8]。
TF-A分为几个二进制文件,每个都有专门的主要角色。 对于32位Arm处理器(AArch32),它分为四个步骤(按执行顺序):
- 引导加载程序第1阶段(BL1)应用处理器受信任的ROM
- 引导加载程序第2阶段(BL2)受信任的引导固件
- 引导加载程序阶段3-2(BL32)运行时软件
- 引导加载程序阶段3-3(BL33)不可信固件
BL1,BL2和BL32是TF-A的一部分。
BL1现在是可选的,并且可以通过启用编译标志BL2_AT_EL3来删除。 然后将其删除以用于STM32MP1,因为所有BL1任务均由 ROM code或BL2完成。 BL33在TF-A之外。 这是TF-A加载的第一个非安全代码。 在引导过程中,这是二级引导加载程序(SSBL)。 对于STM32 MPU平台,默认情况下,SSBL为U-Boot。
TF-A可以使用device tree管理其配置,因为STM32MP1就是这种情况。它是Linux内核的简化版本,仅在引导过程中使用设备。可以使用STM32CubeMX进行配置。
在意法半导体(STMicroelectronics)的实现中,将2个二进制文件BL2和BL32以及设备树放到一个二进制文件中,然后通过ROM代码立即将其加载到SYSRAM中。
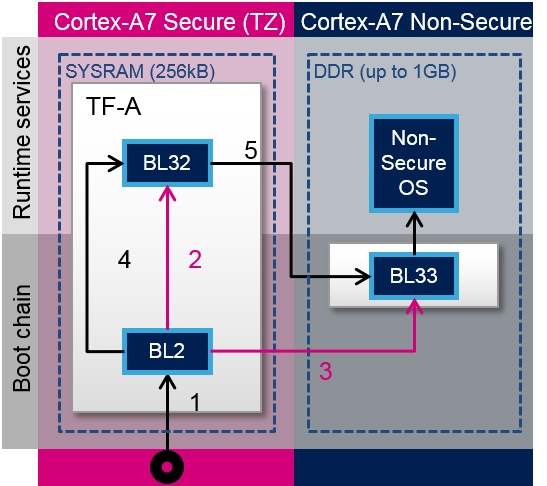
TF-A加载步骤:
- ROM代码加载TF-A二进制文件并调用BL2
- BL2准备BL32
- BL2加载BL33
- BL2呼叫BL32
- BL32呼叫BL33
Boot loader stages
BL1
BL1是第一个执行阶段,设计为充当ROM代码;它在内部RAM中加载和执行。 不适用于STM32MP1。由于STM32MP1具有其专有的 ROM code,因此可以删除此部分,然后BL2是第一个要执行的TF-A二进制文件。
BL2
BL2(受信任的引导固件)负责加载下一阶段的映像(安全和不安全)。 为了实现此作用,BL2必须初始化所有必需的外围设备。
它必须初始化安全组件。
对于STM32MP15,这些安全外围设备为:
- 引导和安全性以及OTP控制 (BSEC internal peripheral)
- 扩展的TrustZone保护控制器(ETZPC internal peripheral)
- DDR的TrustZone地址空间控制器(TZC internal peripheral)
BL2还负责初始化DDR和时钟树。
引导外围设备必须初始化。
在STM32MP15上,它可以是以下之一:
- 通过SDMMC internal peripheral的SD卡
- 通过SDMMC internal peripheral的eMMC
- 通过FMC internal peripheral进行NAND
- NOR通过QUADSPI internal peripheral
在使用中闪烁时使用USB (OTG internal peripheral) 或 UART(USART internal peripheral) , 有关更多详细信息,请参见STM32CubeProgrammer。
BL2还集成了图像验证和身份验证。通过调用BootROM验证服务来实现身份验证。
在执行结束时,在加载BL32和下一个引导阶段(BL33)之后,BL2跳至BL32。
BL32
BL32提供运行时安全服务。在TF-A中,BL32的默认实现是SP_min解决方案。 在TF-A功能列表 [3] 中将其描述为: “最小的AArch32安全有效载荷(SP_MIN),用于演示PSCI [4] 库与AArch32 EL3运行时软件的集成。”
可以用可信任的OS或可信任的环境执行(TEE)代替此最小实现,例如OP-TEE。
STMicroelectronics针对STM32MP1支持两种解决方案(SP_min或OP-TEE)。
BL32充当安全监视器,从而为非安全OS提供安全服务。 这些服务由具有安全监视器调用的非安全软件调用 [6].
此代码负责标准服务呼叫,例如PSCI[4].
它还提供 STMicroelectronics 专用服务, 以访问安全外围设备。 在STM32MP1上,这些服务用于访问 RCC internal peripheral, PWR internal peripheral, RTC internal peripheral 或 BSEC internal peripheral.
References
- ↑ https://www.trustedfirmware.org/
- ↑ https://github.com/ARM-software/arm-trusted-firmware
- ↑ 3.03.1 readme.rst| |}} readme.rst
- ↑ 4.04.14.2 http://infocenter.arm.com/help/topic/com.arm.doc.den0022d/Power_State_Coordination_Interface_PDD_v1_1_DEN0022D.pdf
- ↑ Arm DEN0006C-1
- ↑ 6.06.1 http://infocenter.arm.com/help/topic/com.arm.doc.den0028b/ARM_DEN0028B_SMC_Calling_Convention.pdf
- ↑ http://infocenter.arm.com/help/topic/com.arm.doc.den0056a/DEN0056A_System_Control_and_Management_Interface.pdf
- ↑ docs/firmware-design.rst| |}} docs/firmware-design.rst