“ALSA overview”的版本间的差异
| 第77行: | 第77行: | ||
==How to use== | ==How to use== | ||
| − | + | alsa-utils pakage提供了一组实用程序来管理Linux内核中的音频设备:[https://linux.die.net/man/1/aplay aplay], [https://linux.die.net/man/1/arecord arecord], [https://linux.die.net/man/1/amixer amixer], [https://linux.die.net/man/1/iecset iecset] 和 [https://linux.die.net/man/1/alsactl alsactl]。这些实用程序的概述如下: | |
| − | |||
=== Playback === | === Playback === | ||
*List playback devices | *List playback devices | ||
2020年11月5日 (四) 09:02的版本
本文提供有关高级Linux声音体系结构(ALSA)的信息,该体系结构为Linux操作系统提供音频功能。
目录
Purpose
本文的目的是介绍ALSA框架。
ALSA框架为Linux提供了全面的音频功能,包括音频流的录制和播放,模拟或数字格式,以及路由和混合功能。 ALSA还支持音频中间件,如 PulseAudio, Gstreamer或Android。
System overview
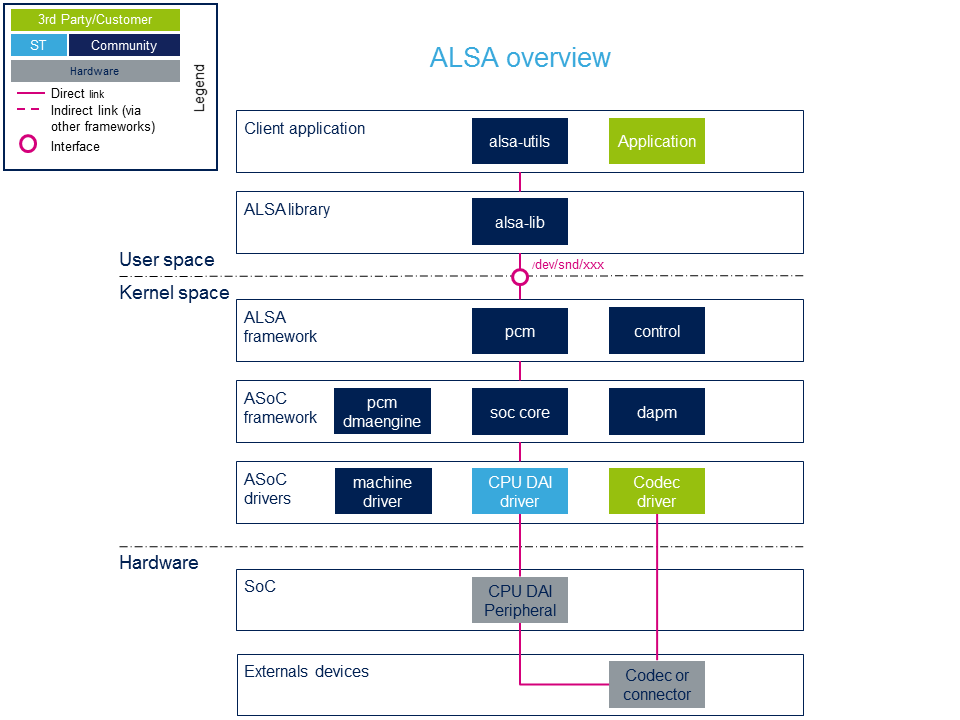
Component descriptions
- alsa-utils (用户空间)
Linux社区提供的ALSA实用程序包包含用于ALSA项目的命令行实用程序(aplay, arecord, amixer, alsamixer ...). 这些工具对于控制声卡很有用。 它们还提供了用于应用程序实现的ALSA API使用示例。
- alsa-lib (User space)
ALSA库软件包包含需要访问ALSA声音接口的程序 (例如alsa-utils程序) 使用的ALSA库。ALSA库在内核模块提供的音频设备上提供了一个抽象级别,例如PCM和控制抽象。
- ALSA framework (Kernel space)
ALSA内核提供了一个API,用于实现音频驱动程序和PCM /控制接口,以在用户区公开音频设备。 PCM接口处理数据流和控制。 该界面管理由ALSA驱动程序导出的控件(音频路径,音量...)。
- ASoC framework (ALSA System On Chip) (Kernel space)
ALSA片上系统(ASoC)层的作用[1]是为了改进 ALSA支持嵌入式片上系统处理器和音频编解码器。 ASoC框架提供了一个DMA引擎,该引擎与DMA框架接口以处理音频样本的传输。ASoC还通过DAPM驱动程序支持音频路径的动态电源管理。 ASoC充当ALSA驱动程序,它将嵌入式音频系统分为三种与平台无关的驱动程序:CPU DAI,编解码器和机器驱动程序。
- ASoC drivers (Kernel space)
ASoC驱动程序允许为ASoC驱动程序类实现与硬件相关的代码:
-
- Codec drivers:
- 这些驱动程序是后端音频组件的驱动程序。 (请参阅下面的编解码器外围设备)
-
- CPU DAI drivers:
- 每个STM32音频外设都有一个特定的CPU DAI驱动程序(请参阅下面的CPU DAI外围设备) 每个CPU DAI至少支持以下协议之一:I2S,PCM或S / PDIF。
-
- Machine drivers:
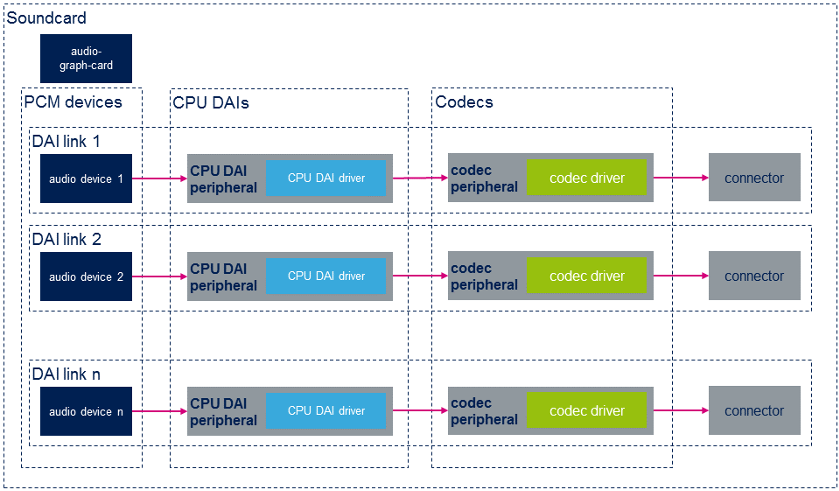
下面的示意图说明了ASoC声卡的总体布局。 请参阅 soundcard configuration 以查看STM32 MPU板的声卡实现示例。
- CPU DAI外围设备 (硬件)
- ST微处理器外围设备提供CPU音频接口。 音频内部外围设备列表可在Audio peripherals section中找到。
- 编解码器外围设备 (硬件)
- 编解码器外设是外部(无CPU)硬件音频I / O设备 (即音频编解码器IC,数字麦克风,放大器,简单的IO连接器...).
Configuration
- 内核配置
如下所示,必须在内核配置中启用ALSA / ASoC和音频图形卡,以启用声音支持。最重要的是,用户必须根据所选的硬件激活CPU和编解码器驱动程序。 用户可以使用Linux Menuconfig tool 以选择所需的驱动程序:
[*] Device Drivers
[*] Sound card support
[*] Advanced Linux Sound Architecture
[*] ALSA for SoC audio support
STMicroelectronics STM32 SOC audio support
[ ] STM32 SAI interface (Serial Audio Interface) support
[ ] STM32 I2S interface (SPI/I2S block) support
[ ] STM32 S/PDIF receiver (SPDIFRX) support
CODEC drivers
[ ] ...
[*] ASoC Audio Graph sound card support
- 设备树配置
通过 device tree中的声卡配置来配置音频子系统。soundcard configuration 文章描述了各种板上可用于STM32MPU的声卡。 本文详细介绍了如何配置用于实现声卡的audio peripherals。
How to use
alsa-utils pakage提供了一组实用程序来管理Linux内核中的音频设备:aplay, arecord, amixer, iecset 和 alsactl。这些实用程序的概述如下:
Playback
- List playback devices
Board $> aplay -l
- Play a wav file on card [X] device [Y]
Board $> aplay -D hw:[X],[Y] <filename.wav>
- Play a wav file or a generated signal on card [X] device [Y]
Board $> speaker-test -D hw:[X],[Y]
Refer to How to play audio article, to find examples of playback use cases on STM32MPU boards.
Record
- List record devices
Board $> arecord -l
- Capture audio from card [X] device [Y]
Board $> arecord -D hw:[X],[Y] -f dat <filename.wav>
Refer to 如何录制音频 article, to find examples of record use cases for the STM32MPU boards.
Controls
- List card [X] controls
Board $> amixer -c [X] controls
- Set card [X] controls [Y] to value [Z]
Board $> amixer -c [X] cset name='[Y]' '[Z]'
- Store soundcard [X] controls state
Board $> alsactl store [X]
- Restore soundcard [X] controls state
Board $> alsactl restore [X]
Refer to Soundcard configuration article to find examples of control configuration for the STM32MPU boards.
IEC controls
- List iec958 parameters
Board $> iecset -h
- Set card [X] iec958 parameter [Y] to value [Z]
Board $> iecset -c [X] cset [Y] [Z]
- Dump card [X] iec958 value
Board $> iecset -c [X] -x
How to trace and debug the framework
This chapter introduces tools useful for debugging and monitoring the audio framework and drivers. It comes as an extension to the top命令 article.
How to monitor
This section introduces ALSA framework monitoring methods. Refer to Linux monitoring tools articles for further information.
Procfs filesystem
The ALSA asound directory[6] in procfs file system, provides a lot of information on sound cards. The PCM proc files, provides useful PCM substream debugging information, such as hardware/software parameters, stream status and buffer information.
Examples:
- List PCM audio devices:
Board $> cat /proc/asound/pcm
- Get hardware parameters of a PCM audio device (device "0" of card "0" here):
Board $> cat /proc/asound/card0/pcm0p/sub0/hw_params
Debugfs filesystem
The asoc directory in 调试文件系统(debugfs) file system provides information on sound card components.
Examples:
- List DAIs
Board $> cat /sys/kernel/debug/asoc/dais
- List DAPMs of "xxx.audio-controller" CPU DAI of "STM32MP1-EV" soundcard
Board $> ls /sys/kernel/debug/asoc/STM32MP1-EV/xxx.audio-controller/dapm
How to trace
This section introduces tracing methods for ALSA framework. Refer to Linux_tracing_tools articles to go further.
Dynamic traces
ALSA framework and driver debug traces can be added to the kernel logs by using the dynamic debug mechanism.
- Example: Activate dynamic trace for SAI Linux driver, and print the traces to the console:
Board $> echo -n 'file stm32_sai.c +p; file stm32_sai_sub.c +p' > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control; Board $> dmesg -n8;
Tracing filesystem
The Linux kernel offers a tracefs filesystem, provided with Linux kernel tracing framework. ALSA and ASoC have their own tracepoints in this tracing filesystem:
- asoc entry for ASoC, provides the DAPM, jack and bias level tracepoints.[7]
- snd_pcm entry for ALSA, provides the PCM buffers and PCM hardware parameters tracepoints[7][8].
Activate DAPM traces
Prerequisite: the CONFIG_FUNCTION_TRACER configuration must first be enabled in the Linux kernel configuration
- Enable trace[7]
Board $> echo '1' > /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/events/asoc/enable
- Check log:
Board $> cat /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/trace
Activate PCM hardware parameter traces
Prerequisite: the CONFIG_FUNCTION_TRACER and CONFIG_SND_DEBUG configurations must first be enabled in the Linux kernel configuration
- Enable trace[7]
Board $> echo '1' > /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/events/snd_pcm/enable
- Check log:
Board $> cat /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/trace
Activate PCM buffer state traces (PCM ring buffer overrun/underrun debugging)
Prerequisite: the CONFIG_FUNCTION_TRACER, CONFIG_SND_DEBUG, CONFIG_SND_DEBUG_VERBOSE and SND_PCM_XRUN_DEBUG configurations must first be enabled in the Linux kernel configuration
- Set XRUN trace verbosity[9]
# Enable basic debugging and stack dump Board $> echo 3 > /proc/asound/card0/pcm0p/xrun_debug
- Enable trace[7]
Board $> echo '1' > /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/events/snd_pcm/enable
- Check log:
Board $> cat /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/trace
How to debug
Refer to the Linux debugging tools articles.
Source code location
User space
References
- ↑ ASoC layer documentation
- ↑ Documentation/devicetree/bindings/sound/audio-graph-card.txt| |}} Documentation/devicetree/bindings/sound/audio-graph-card.txt
- ↑ Documentation/devicetree/bindings/graph.txt| |}} Documentation/devicetree/bindings/graph.txt
- ↑ ALSA library API
- ↑ ALSA and ASoC driver API documentation
- ↑ ALSA proc files
- ↑ 7.07.17.27.37.4 Documentation/trace/tracepoint-analysis.rst| |}} Documentation/trace/tracepoint-analysis.rst
- ↑ ALSA tracepoints
- ↑ XRUN Debug
<securetransclude src="ProtectedTemplate:PublicationRequestId" params="10644 | 2019-02-06 | StephenG"></securetransclude> <securetransclude src="ProtectedTemplate:ArticleBasedOnModel" params="Framework overview article model"></securetransclude>