“MTD overview”的版本间的差异
| (未显示同一用户的8个中间版本) | |||
| 第66行: | 第66行: | ||
==Configuration == | ==Configuration == | ||
===Kernel configuration=== | ===Kernel configuration=== | ||
| − | + | ST交货中默认激活MTD。 但是,如果需要特定的配置,则本节说明如何在内核中激活/停用MTD。 | |
| − | + | 使用Linux Menuconfig工具在内核配置中激活MTD:[[Menuconfig or how to configure kernel]]. | |
==== SLC NAND Flash memory ==== | ==== SLC NAND Flash memory ==== | ||
| 第92行: | 第92行: | ||
===Device tree configuration=== | ===Device tree configuration=== | ||
| − | + | 借助[[STM32CubeMX]]可以完成DT配置。 | |
==== NAND Flash memory ==== | ==== NAND Flash memory ==== | ||
| − | + | 请参考 [[FMC_device_tree_configuration| FMC device tree configuration]]. | |
==== SPI NOR/NAND Flash memory ==== | ==== SPI NOR/NAND Flash memory ==== | ||
| − | + | 请参考 [[QUADSPI_device_tree_configuration| QUADSPI device tree configuration]]. | |
== How to use the framework == | == How to use the framework == | ||
| − | + | 可以在MTD框架上使用处理读/写/擦除操作的文件系统。 请参考[[How to support UBIFS through MTD|UBIFS support through MTD]]. | |
| − | + | 您还可以使用MTD实用程序与MTD子系统进行交互。 | |
| − | + | MTD实用程序<ref>[http://www.linux-mtd.infradead.org MTD utils]</ref> 是一组工具,可用于通过MTD字符接口对闪存执行操作。 | |
| − | + | 最常用的实用程序是: | |
| − | |||
* mtdinfo | * mtdinfo | ||
* flash_erase | * flash_erase | ||
| 第215行: | 第214行: | ||
===How to monitor=== | ===How to monitor=== | ||
| − | + | sysfs界面提供有关每个mtd设备的详细信息。 | |
root:~# cat /sys/class/mtd/mtd0/name | root:~# cat /sys/class/mtd/mtd0/name | ||
| 第231行: | 第230行: | ||
===How to trace=== | ===How to trace=== | ||
| − | + | 详细动态跟踪可在此处 [[How to use the kernel dynamic debug]]. | |
root:~# echo "file drivers/mtd/* +p" > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control | root:~# echo "file drivers/mtd/* +p" > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control | ||
==Source code location== | ==Source code location== | ||
| − | + | MTD框架为{{CodeSource | Linux kernel | drivers/mtd | here}}. | |
==To go further== | ==To go further== | ||
| − | + | 请参阅MTD常见问题解答文档 <ref>[http://www.linux-mtd.infradead.org/faq/general.html MTD FAQs]</ref>. | |
==References== | ==References== | ||
| − | + | 有关完整说明,请参阅以下链接: | |
<references /> | <references /> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
2020年11月11日 (三) 11:51的最新版本
SUMMARY
MTD(内存技术设备)子系统为原始闪存提供抽象层。 在使用不同的Flash类型和技术(例如,Flash)时,可以使用相同的API。 SLC NAND,SPI NOR,...
目录
Framework purpose
本文的目的是介绍MTD Linux子系统:
- 一般信息
- 主要组成部分/利益相关者
- 如何使用MTD API
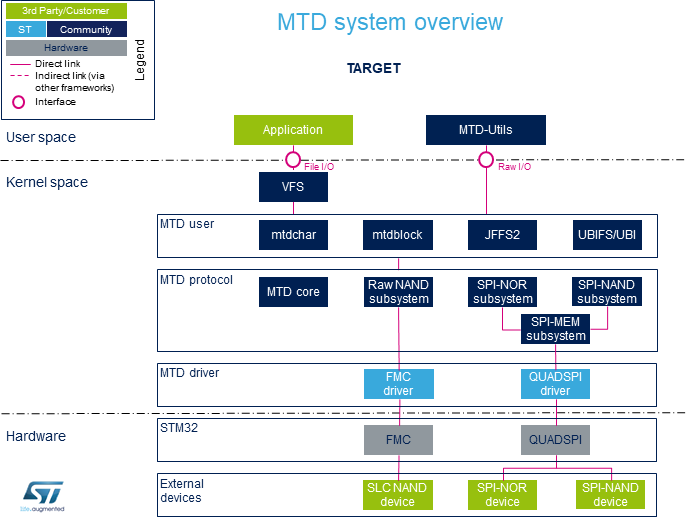
System overview
Component description
- 执行“文件I / O”的用户空间应用程序需要像对待磁盘一样查看闪存,而希望完成“原始I / O”的程序就像访问磁盘一样访问该存储器。 是一个角色设备。
- VFS (内核空间)
虚拟文件系统。 请参考VFS文档 [1].
- mtdchar (内核空间)
通常称为/ dev / mtdX。 对于MTD字符设备,请参考MTD概述文档 [2].
- mtdblock (内核空间)
通常称为/ dev / mtdblockX。 除非您确切知道自己在做什么,否则不要使用mtdblock。 对于MTD块设备,请参考MTD块文档[3].
- JFFS2 (内核空间)
日记Flash文件系统。 请参考MTD JFFS2文档 [4].
- UBI (内核空间)
未分类的块图像。 请参考MTD UBI文档 [5].
- UBIFS (内核空间)
UBI文件系统。 请参考MTD UBIFS文档[6].
- MTD core (内核空间)
MTD内核为原始闪存提供了一个抽象层。
- Raw NAND subsystem (内核空间)
MTD子系统中使用Raw NAND协议来连接NAND闪存。
- SPI-MEM subsystem (内核空间)
SPI-MEM协议在MTD子系统中用于连接各种SPI存储器(NOR,NAND)
- SPI-NAND subsystem (内核空间)
SPI-NAND协议在MTD子系统中用于连接SPI NAND闪存。
- SPI-NOR subsystem (内核空间)
MTD子系统中使用SPI-NOR协议来连接SPI NOR闪存。
- FMC driver (内核空间) / FMC (硬件)
- QUADSPI driver (Kernel space) / QUADSPI (Hardware)
API description
有关Linux MTD API的描述,请参阅MTD API文档 [7].
Configuration
Kernel configuration
ST交货中默认激活MTD。 但是,如果需要特定的配置,则本节说明如何在内核中激活/停用MTD。
使用Linux Menuconfig工具在内核配置中激活MTD:Menuconfig or how to configure kernel.
SLC NAND Flash memory
[*] Device Drivers --->
<*> Memory Technology Device (MTD) support --->
<*> RAW/Parallel NAND Device Support --->
<*> Support for NAND controller on STM32MP Socs.
SPI NOR/NAND Flash memory
[*] Device Drivers --->
<*> Memory Technology Device (MTD) support --->
Self-contained MTD device drivers --->
<*> Support most SPI Flash chips (AT26DF, M25P, W25X, ...)
<*> SPI NAND device Support
<*> SPI-NOR device support
<*> SPI support --->
-*- SPI memory extension
<*> STMicroelectronics STM32 QUAD SPI controller
How to use the framework
可以在MTD框架上使用处理读/写/擦除操作的文件系统。 请参考UBIFS support through MTD.
您还可以使用MTD实用程序与MTD子系统进行交互。 MTD实用程序[8] 是一组工具,可用于通过MTD字符接口对闪存执行操作。 最常用的实用程序是:
- mtdinfo
- flash_erase
- flashcp
- nandwrite
- nanddump
root:~# mtdinfo -a Count of MTD devices: 9 Present MTD devices: mtd0, mtd1, mtd2, mtd3, mtd4, mtd5, mtd6, mtd7, mtd8 Sysfs interface supported: yes
mtd0 Name: fsbl Type: nand Eraseblock size: 262144 bytes, 256.0 KiB Amount of eraseblocks: 8 (2097152 bytes, 2.0 MiB) Minimum input/output unit size: 4096 bytes Sub-page size: 4096 bytes OOB size: 224 bytes Character device major/minor: 90:0 Bad blocks are allowed: true Device is writable: true
mtd1 Name: ssbl Type: nand Eraseblock size: 262144 bytes, 256.0 KiB Amount of eraseblocks: 8 (2097152 bytes, 2.0 MiB) Minimum input/output unit size: 4096 bytes Sub-page size: 4096 bytes OOB size: 224 bytes Character device major/minor: 90:2 Bad blocks are allowed: true Device is writable: true
mtd2 Name: UBI Type: nand Eraseblock size: 262144 bytes, 256.0 KiB Amount of eraseblocks: 4078 (1069023232 bytes, 1019.5 MiB) Minimum input/output unit size: 4096 bytes Sub-page size: 4096 bytes OOB size: 224 bytes Character device major/minor: 90:4 Bad blocks are allowed: true Device is writable: true
mtd3 Name: fsbl1 Type: nor Eraseblock size: 65536 bytes, 64.0 KiB Amount of eraseblocks: 4 (262144 bytes, 256.0 KiB) Minimum input/output unit size: 1 byte Sub-page size: 1 byte Character device major/minor: 90:6 Bad blocks are allowed: false Device is writable: true
mtd4 Name: fsbl2 Type: nor Eraseblock size: 65536 bytes, 64.0 KiB Amount of eraseblocks: 4 (262144 bytes, 256.0 KiB) Minimum input/output unit size: 1 byte Sub-page size: 1 byte Character device major/minor: 90:8 Bad blocks are allowed: false Device is writable: true
mtd5 Name: ssbl Type: nor Eraseblock size: 65536 bytes, 64.0 KiB Amount of eraseblocks: 32 (2097152 bytes, 2.0 MiB) Minimum input/output unit size: 1 byte Sub-page size: 1 byte Character device major/minor: 90:10 Bad blocks are allowed: false Device is writable: true
mtd6 Name: logo Type: nor Eraseblock size: 65536 bytes, 64.0 KiB Amount of eraseblocks: 4 (262144 bytes, 256.0 KiB) Minimum input/output unit size: 1 byte Sub-page size: 1 byte Character device major/minor: 90:12 Bad blocks are allowed: false Device is writable: true
mtd7 Name: nor_user Type: nor Eraseblock size: 65536 bytes, 64.0 KiB Amount of eraseblocks: 980 (64225280 bytes, 61.2 MiB) Minimum input/output unit size: 1 byte Sub-page size: 1 byte Character device major/minor: 90:14 Bad blocks are allowed: false Device is writable: true
mtd8 Name: 58003000.qspi Type: nor Eraseblock size: 65536 bytes, 64.0 KiB Amount of eraseblocks: 1024 (67108864 bytes, 64.0 MiB) Minimum input/output unit size: 1 byte Sub-page size: 1 byte Character device major/minor: 90:16 Bad blocks are allowed: false Device is writable: true
How to trace and debug the framework
How to monitor
sysfs界面提供有关每个mtd设备的详细信息。
root:~# cat /sys/class/mtd/mtd0/name fsbl root:~# cat /sys/class/mtd/mtd0/type nand root:~# cat /sys/class/mtd/mtd0/erasesize 262144 root:~# cat /sys/class/mtd/mtd0/ecc_strength 8 root:~# cat /sys/class/mtd/mtd0/bad_blocks 0 root:~# cat /sys/class/mtd/mtd0/ecc_failures 0
How to trace
详细动态跟踪可在此处 How to use the kernel dynamic debug.
root:~# echo "file drivers/mtd/* +p" > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control
Source code location
MTD框架为drivers/mtd | |}} here .
To go further
请参阅MTD常见问题解答文档 [9].