“ALSA overview”的版本间的差异
(→Record) |
|||
| (未显示同一用户的3个中间版本) | |||
| 第99行: | 第99行: | ||
=== Controls === | === Controls === | ||
| − | * | + | *列表卡[X]控件 |
'''Board $>''' amixer -c [X] controls | '''Board $>''' amixer -c [X] controls | ||
| − | * | + | *将卡[X]的控件[Y]设置为[Z] |
'''Board $>''' amixer -c [X] cset name='[Y]' '[Z]' | '''Board $>''' amixer -c [X] cset name='[Y]' '[Z]' | ||
| − | * | + | *存储声卡[X]控制状态 |
'''Board $>''' alsactl store [X] | '''Board $>''' alsactl store [X] | ||
| − | * | + | *恢复声卡[ x ]控件状态 |
'''Board $>''' alsactl restore [X] | '''Board $>''' alsactl restore [X] | ||
| − | + | 请参阅[ [[Soundcard configuration]] 文章,以找到STM32MPU板的控制配置示例。 | |
=== IEC controls === | === IEC controls === | ||
| − | * | + | *列出iec958参数 |
'''Board $>''' iecset -h | '''Board $>''' iecset -h | ||
| − | * | + | *将卡[X] iec958参数[Y]设置为值[Z] |
'''Board $>''' iecset -c [X] cset [Y] [Z] | '''Board $>''' iecset -c [X] cset [Y] [Z] | ||
| − | * | + | *转储卡[X] iec958值 |
'''Board $>''' iecset -c [X] -x | '''Board $>''' iecset -c [X] -x | ||
==How to trace and debug the framework== | ==How to trace and debug the framework== | ||
| − | + | 本章介绍了可用于调试和监视音频框架和驱动程序的工具。 它是 [[Linux_tracing,_monitoring_and_debugging]] 文章的扩展。 | |
=== How to monitor === | === How to monitor === | ||
| − | + | 本节介绍ALSA框架监视方法。 有关更多信息,请参阅[[:Category:Linux monitoring tools|Linux monitoring tools]]文章。 | |
| − | |||
==== Procfs filesystem ==== | ==== Procfs filesystem ==== | ||
| − | + | ALSA'''asound'''目录<ref>[https://www.kernel.org/doc/html/latest/sound/designs/procfile.html ALSA proc files]</ref> 在 [[Pseudo_filesystem|procfs]] 文件系统中, 提供了大量有关声卡的信息。 PCM proc文件提供有用的PCM子流调试信息,例如硬件/软件参数,流状态和缓冲区信息。 | |
| − | + | 示例: | |
| − | + | :* 列出PCM音频设备: | |
| − | :* | ||
<div style="margin-left: 2em;"> | <div style="margin-left: 2em;"> | ||
'''Board $>''' cat /proc/{{highlight|asound}}/pcm | '''Board $>''' cat /proc/{{highlight|asound}}/pcm | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | :* | + | :* 获取PCM音频设备的硬件参数(此处为卡0的设备0): |
<div style="margin-left: 2em;"> | <div style="margin-left: 2em;"> | ||
'''Board $>''' cat /proc/{{highlight|asound}}/card0/pcm0p/sub0/hw_params | '''Board $>''' cat /proc/{{highlight|asound}}/card0/pcm0p/sub0/hw_params | ||
| 第138行: | 第136行: | ||
==== Debugfs filesystem ==== | ==== Debugfs filesystem ==== | ||
| − | + | [[Debugfs|debugfs]]文件系统中的'''asoc'''目录提供有关声卡组件的信息。 | |
| − | + | 示例: | |
:* List DAIs | :* List DAIs | ||
<div style="margin-left: 2em;"> | <div style="margin-left: 2em;"> | ||
| 第146行: | 第144行: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | :* | + | :* 列出 "xxx.audio-controller"声卡的 "{{highlight|STM32MP1-EV}}" CPU DAI的DAPM |
<div style="margin-left: 2em;"> | <div style="margin-left: 2em;"> | ||
'''Board $>''' ls /sys/kernel/debug/{{highlight|asoc}}/{{highlight|STM32MP1-EV}}/xxx.audio-controller/dapm | '''Board $>''' ls /sys/kernel/debug/{{highlight|asoc}}/{{highlight|STM32MP1-EV}}/xxx.audio-controller/dapm | ||
| 第152行: | 第150行: | ||
=== How to trace === | === How to trace === | ||
| − | + | 本节介绍了ALSA框架的跟踪方法。参见 [[:Category:Linux_tracing_tools|Linux_tracing_tools]] 文章将进一步。 | |
==== Dynamic traces ==== | ==== Dynamic traces ==== | ||
| − | + | 可以使用 [[How_to_use_the_kernel_dynamic_debug|dynamic debug]] 机制将ALSA框架和驱动程序调试跟踪添加到内核日志中。 | |
| − | * | + | * 示例:启动SAI Linux驱动的动态跟踪,并将跟踪打印到控制台: |
'''Board $>''' echo -n 'file stm32_sai.c +p; file stm32_sai_sub.c +p' > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control; | '''Board $>''' echo -n 'file stm32_sai.c +p; file stm32_sai_sub.c +p' > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control; | ||
| 第162行: | 第160行: | ||
==== Tracing filesystem ==== | ==== Tracing filesystem ==== | ||
| − | + | Linux内核提供了 [[Pseudo_filesystem|tracefs]] 文件系统,并随Linux内核跟踪框架一起提供。 ALSA和ASoC在此跟踪文件系统中具有自己的跟踪点: | |
| − | * '''asoc''' | + | * ASoC的'''asoc''' 条目提供了DAPM,插孔和偏置电平跟踪点。<ref name="tracepoints">{{CodeSource | Linux kernel | Documentation/trace/tracepoint-analysis.rst}}</ref> |
| − | * '''snd_pcm''' | + | * ALSA的'''snd_pcm'''条目,提供了PCM缓冲区和PCM硬件参数跟踪点<ref name="tracepoints"></ref><ref name="tracepoints_pcm">[https://www.kernel.org/doc/html/latest/sound/designs/tracepoints.html ALSA tracepoints]</ref>. |
===== Activate DAPM traces ===== | ===== Activate DAPM traces ===== | ||
| − | + | 先决条件:必须首先在 [[Menuconfig or how to configure kernel | Linux kernel configuration]]中启用CONFIG_FUNCTION_TRACER配置 | |
| − | * | + | * 启用追踪<ref name="tracepoints"></ref> |
'''Board $>''' echo '1' > /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/events/{{highlight|asoc}}/enable | '''Board $>''' echo '1' > /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/events/{{highlight|asoc}}/enable | ||
| − | * | + | * 检查日志: |
'''Board $>''' cat /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/trace | '''Board $>''' cat /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/trace | ||
===== Activate PCM hardware parameter traces ===== | ===== Activate PCM hardware parameter traces ===== | ||
| − | + | 先决条件:必须首先在 [[Menuconfig or how to configure kernel | Linux kernel configuration]]中启用CONFIG_FUNCTION_TRACER和CONFIG_SND_DEBUG配置。 | |
| − | * | + | * 启用追踪<ref name="tracepoints"></ref> |
'''Board $>''' echo '1' > /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/events/{{highlight|snd_pcm}}/enable | '''Board $>''' echo '1' > /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/events/{{highlight|snd_pcm}}/enable | ||
| − | * | + | * 检查日志: |
'''Board $>''' cat /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/trace | '''Board $>''' cat /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/trace | ||
===== Activate PCM buffer state traces (PCM ring buffer overrun/underrun debugging) ===== | ===== Activate PCM buffer state traces (PCM ring buffer overrun/underrun debugging) ===== | ||
| − | + | 先决条件:必须首先在 [[Menuconfig or how to configure kernel | Linux kernel configuration]]中启用CONFIG_Function_TRACE、CONFIG_SND_DEBUG、CONFIG_SND_DEBUG_VERBOSE和SND_PCM_XRUN_DEBUG配置 | |
| − | * | + | * 设置XRUN跟踪详细程度<ref>[http://www.alsa-project.org/main/index.php/XRUN_Debug XRUN Debug]</ref> |
| − | # | + | # 启用基本调试和堆栈转储 |
'''Board $>''' echo 3 > /proc/asound/card0/pcm0p/xrun_debug | '''Board $>''' echo 3 > /proc/asound/card0/pcm0p/xrun_debug | ||
| − | * | + | * 启用追踪<ref name="tracepoints"></ref> |
'''Board $>''' echo '1' > /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/events/{{highlight|snd_pcm}}/enable | '''Board $>''' echo '1' > /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/events/{{highlight|snd_pcm}}/enable | ||
| − | * | + | * 检查日志: |
'''Board $>''' cat /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/trace | '''Board $>''' cat /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/trace | ||
=== How to debug === | === How to debug === | ||
| − | + | 请参阅 [[:Category:Linux debugging tools|Linux debugging tools]] 文章。 | |
==Source code location== | ==Source code location== | ||
| 第209行: | 第207行: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
2020年11月5日 (四) 10:00的最新版本
本文提供有关高级Linux声音体系结构(ALSA)的信息,该体系结构为Linux操作系统提供音频功能。
目录
Purpose
本文的目的是介绍ALSA框架。
ALSA框架为Linux提供了全面的音频功能,包括音频流的录制和播放,模拟或数字格式,以及路由和混合功能。 ALSA还支持音频中间件,如 PulseAudio, Gstreamer或Android。
System overview
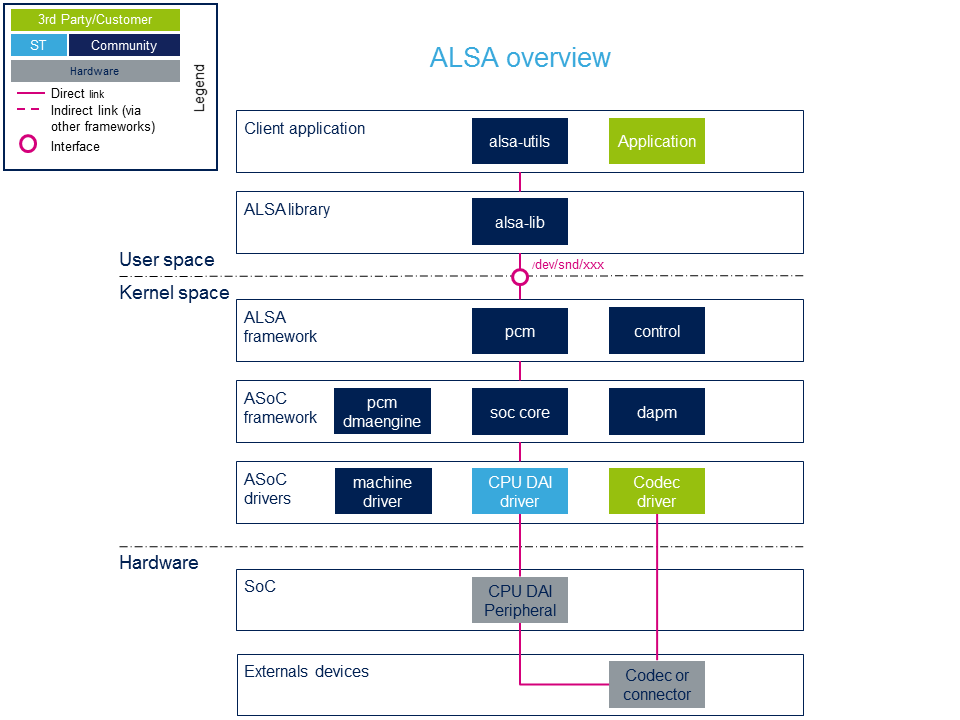
Component descriptions
- alsa-utils (用户空间)
Linux社区提供的ALSA实用程序包包含用于ALSA项目的命令行实用程序(aplay, arecord, amixer, alsamixer ...). 这些工具对于控制声卡很有用。 它们还提供了用于应用程序实现的ALSA API使用示例。
- alsa-lib (User space)
ALSA库软件包包含需要访问ALSA声音接口的程序 (例如alsa-utils程序) 使用的ALSA库。ALSA库在内核模块提供的音频设备上提供了一个抽象级别,例如PCM和控制抽象。
- ALSA framework (Kernel space)
ALSA内核提供了一个API,用于实现音频驱动程序和PCM /控制接口,以在用户区公开音频设备。 PCM接口处理数据流和控制。 该界面管理由ALSA驱动程序导出的控件(音频路径,音量...)。
- ASoC framework (ALSA System On Chip) (Kernel space)
ALSA片上系统(ASoC)层的作用[1]是为了改进 ALSA支持嵌入式片上系统处理器和音频编解码器。 ASoC框架提供了一个DMA引擎,该引擎与DMA框架接口以处理音频样本的传输。ASoC还通过DAPM驱动程序支持音频路径的动态电源管理。 ASoC充当ALSA驱动程序,它将嵌入式音频系统分为三种与平台无关的驱动程序:CPU DAI,编解码器和机器驱动程序。
- ASoC drivers (Kernel space)
ASoC驱动程序允许为ASoC驱动程序类实现与硬件相关的代码:
-
- Codec drivers:
- 这些驱动程序是后端音频组件的驱动程序。 (请参阅下面的编解码器外围设备)
-
- CPU DAI drivers:
- 每个STM32音频外设都有一个特定的CPU DAI驱动程序(请参阅下面的CPU DAI外围设备) 每个CPU DAI至少支持以下协议之一:I2S,PCM或S / PDIF。
-
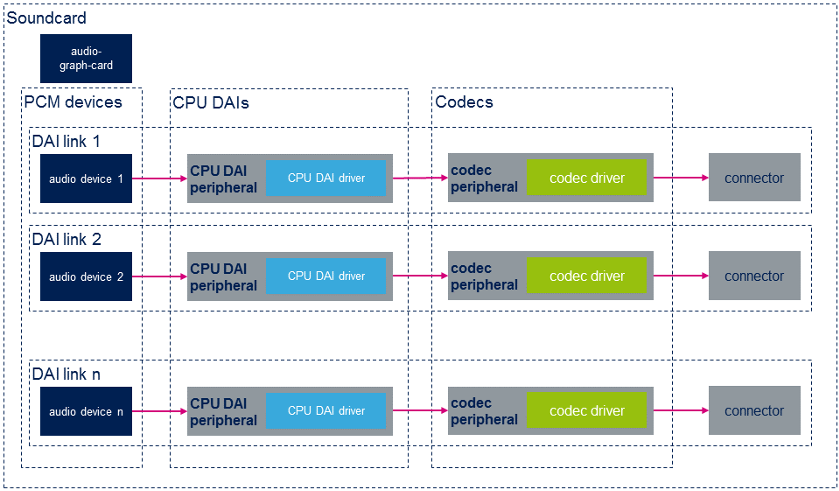
- Machine drivers:
下面的示意图说明了ASoC声卡的总体布局。 请参阅 soundcard configuration 以查看STM32 MPU板的声卡实现示例。
- CPU DAI外围设备 (硬件)
- ST微处理器外围设备提供CPU音频接口。 音频内部外围设备列表可在Audio peripherals section中找到。
- 编解码器外围设备 (硬件)
- 编解码器外设是外部(无CPU)硬件音频I / O设备 (即音频编解码器IC,数字麦克风,放大器,简单的IO连接器...).
Configuration
- 内核配置
如下所示,必须在内核配置中启用ALSA / ASoC和音频图形卡,以启用声音支持。最重要的是,用户必须根据所选的硬件激活CPU和编解码器驱动程序。 用户可以使用Linux Menuconfig tool 以选择所需的驱动程序:
[*] Device Drivers
[*] Sound card support
[*] Advanced Linux Sound Architecture
[*] ALSA for SoC audio support
STMicroelectronics STM32 SOC audio support
[ ] STM32 SAI interface (Serial Audio Interface) support
[ ] STM32 I2S interface (SPI/I2S block) support
[ ] STM32 S/PDIF receiver (SPDIFRX) support
CODEC drivers
[ ] ...
[*] ASoC Audio Graph sound card support
- 设备树配置
通过 device tree中的声卡配置来配置音频子系统。soundcard configuration 文章描述了各种板上可用于STM32MPU的声卡。 本文详细介绍了如何配置用于实现声卡的audio peripherals。
How to use
alsa-utils pakage提供了一组实用程序来管理Linux内核中的音频设备:aplay, arecord, amixer, iecset 和 alsactl。这些实用程序的概述如下:
Playback
- 列出播放设备
Board $> aplay -l
- 在卡[X]设备[Y]上播放wav文件
Board $> aplay -D hw:[X],[Y] <filename.wav>
- 在卡[X]设备[Y]上播放wav文件或生成的信号
Board $> speaker-test -D hw:[X],[Y]
请参阅How to play audio 一文,以查找STM32MPU板上的回放用例示例。
Record
- 列出记录设备
Board $> arecord -l
- 从卡[X]设备[Y]捕获音频
Board $> arecord -D hw:[X],[Y] -f dat <filename.wav>
请参阅 如何录制音频 文章,查找STM32MPU主板的录制用例示例。
Controls
- 列表卡[X]控件
Board $> amixer -c [X] controls
- 将卡[X]的控件[Y]设置为[Z]
Board $> amixer -c [X] cset name='[Y]' '[Z]'
- 存储声卡[X]控制状态
Board $> alsactl store [X]
- 恢复声卡[ x ]控件状态
Board $> alsactl restore [X]
请参阅[ Soundcard configuration 文章,以找到STM32MPU板的控制配置示例。
IEC controls
- 列出iec958参数
Board $> iecset -h
- 将卡[X] iec958参数[Y]设置为值[Z]
Board $> iecset -c [X] cset [Y] [Z]
- 转储卡[X] iec958值
Board $> iecset -c [X] -x
How to trace and debug the framework
本章介绍了可用于调试和监视音频框架和驱动程序的工具。 它是 top命令 文章的扩展。
How to monitor
本节介绍ALSA框架监视方法。 有关更多信息,请参阅Linux monitoring tools文章。
Procfs filesystem
ALSAasound目录[6] 在 procfs 文件系统中, 提供了大量有关声卡的信息。 PCM proc文件提供有用的PCM子流调试信息,例如硬件/软件参数,流状态和缓冲区信息。 示例:
- 列出PCM音频设备:
Board $> cat /proc/asound/pcm
- 获取PCM音频设备的硬件参数(此处为卡0的设备0):
Board $> cat /proc/asound/card0/pcm0p/sub0/hw_params
Debugfs filesystem
调试文件系统(debugfs)文件系统中的asoc目录提供有关声卡组件的信息。
示例:
- List DAIs
Board $> cat /sys/kernel/debug/asoc/dais
- 列出 "xxx.audio-controller"声卡的 "STM32MP1-EV" CPU DAI的DAPM
Board $> ls /sys/kernel/debug/asoc/STM32MP1-EV/xxx.audio-controller/dapm
How to trace
本节介绍了ALSA框架的跟踪方法。参见 Linux_tracing_tools 文章将进一步。
Dynamic traces
可以使用 dynamic debug 机制将ALSA框架和驱动程序调试跟踪添加到内核日志中。
- 示例:启动SAI Linux驱动的动态跟踪,并将跟踪打印到控制台:
Board $> echo -n 'file stm32_sai.c +p; file stm32_sai_sub.c +p' > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control; Board $> dmesg -n8;
Tracing filesystem
Linux内核提供了 tracefs 文件系统,并随Linux内核跟踪框架一起提供。 ALSA和ASoC在此跟踪文件系统中具有自己的跟踪点:
Activate DAPM traces
先决条件:必须首先在 Linux kernel configuration中启用CONFIG_FUNCTION_TRACER配置
- 启用追踪[7]
Board $> echo '1' > /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/events/asoc/enable
- 检查日志:
Board $> cat /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/trace
Activate PCM hardware parameter traces
先决条件:必须首先在 Linux kernel configuration中启用CONFIG_FUNCTION_TRACER和CONFIG_SND_DEBUG配置。
- 启用追踪[7]
Board $> echo '1' > /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/events/snd_pcm/enable
- 检查日志:
Board $> cat /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/trace
Activate PCM buffer state traces (PCM ring buffer overrun/underrun debugging)
先决条件:必须首先在 Linux kernel configuration中启用CONFIG_Function_TRACE、CONFIG_SND_DEBUG、CONFIG_SND_DEBUG_VERBOSE和SND_PCM_XRUN_DEBUG配置
- 设置XRUN跟踪详细程度[9]
# 启用基本调试和堆栈转储 Board $> echo 3 > /proc/asound/card0/pcm0p/xrun_debug
- 启用追踪[7]
Board $> echo '1' > /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/events/snd_pcm/enable
- 检查日志:
Board $> cat /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/trace
How to debug
请参阅 Linux debugging tools 文章。
Source code location
User space
References
- ↑ ASoC layer documentation
- ↑ Documentation/devicetree/bindings/sound/audio-graph-card.txt| |}} Documentation/devicetree/bindings/sound/audio-graph-card.txt
- ↑ Documentation/devicetree/bindings/graph.txt| |}} Documentation/devicetree/bindings/graph.txt
- ↑ ALSA library API
- ↑ ALSA and ASoC driver API documentation
- ↑ ALSA proc files
- ↑ 7.07.17.27.37.4 Documentation/trace/tracepoint-analysis.rst| |}} Documentation/trace/tracepoint-analysis.rst
- ↑ ALSA tracepoints
- ↑ XRUN Debug