“U-Boot overview”的版本间的差异
| 第153行: | 第153行: | ||
== U-Boot command line interface (CLI) == | == U-Boot command line interface (CLI) == | ||
| − | + | 请参阅 [http://www.denx.de/wiki/view/DULG/UBootCommandLineInterface U-Boot Command Line Interface]. | |
| − | + | 如果CONFIG_AUTOBOOT已激活,则在显示以下行并执行[[#bootcmd|bootcmd]](CONFIG_BOOTCOMMAND)后,您有CONFIG_BOOTDELAY秒(默认情况下为2秒)通过按任意键进入控制台: | |
| − | Hit any key to stop autoboot: | + | Hit any key to stop autoboot: 2 |
=== Commands === | === Commands === | ||
| − | + | 这些命令在{{CodeSource | U-Boot | cmd/ | cmd/*.c}}. 通过相应的 '''CONFIG_CMD_*''' 配置标志激活它们。 | |
| − | + | 使用U-Boot shell中的<code>help</code> 命令列出设备上可用的命令: | |
{{Board$}} help | {{Board$}} help | ||
| − | + | 以下是从中提取的所有命令的列表 [http://www.denx.de/wiki/view/DULG/Manual U-Boot Manual] ('''不详尽'''): | |
* [http://www.denx.de/wiki/view/DULG/UBootCmdGroupInfo Information Commands] | * [http://www.denx.de/wiki/view/DULG/UBootCmdGroupInfo Information Commands] | ||
| − | ** bdinfo - | + | ** bdinfo - 打印板信息结构 |
| − | ** coninfo - | + | ** coninfo - 打印控制台设备和信息 |
| − | ** flinfo - | + | ** flinfo - 打印闪存信息 |
| − | ** iminfo - | + | ** iminfo - 打印应用程序映像的标题信息 |
| − | ** help - | + | ** help - 打印在线帮助 |
* [http://www.denx.de/wiki/view/DULG/UBootCmdGroupMemory Memory Commands] | * [http://www.denx.de/wiki/view/DULG/UBootCmdGroupMemory Memory Commands] | ||
| − | ** base - | + | ** base - 打印或设置地址偏移量 |
| − | ** crc32 - | + | ** crc32 - 校验和计算 |
| − | ** cmp - | + | ** cmp - 内存比较 |
| − | ** cp - | + | ** cp - 内存拷贝 |
| − | ** md - | + | ** md - 内存显示 |
| − | ** mm - | + | ** mm - 内存修改(自动递增) |
| − | ** mtest - | + | ** mtest - 简单的RAM测试 |
| − | ** mw - | + | ** mw - 内存写入(填充) |
| − | ** nm - | + | ** nm - 内存修改(常量地址) |
| − | ** loop - | + | ** loop - 地址范围内无限循环 |
* [http://www.denx.de/wiki/view/DULG/UBootCmdGroupFlash Flash Memory Commands] | * [http://www.denx.de/wiki/view/DULG/UBootCmdGroupFlash Flash Memory Commands] | ||
| − | ** cp - | + | ** cp - 内存复制 |
| − | ** flinfo - | + | ** flinfo - 打印闪存信息 |
| − | ** erase - | + | ** erase - 清除闪存 |
| − | ** protect - | + | ** protect - 启用或禁用闪存写入保护 |
| − | ** mtdparts - | + | ** mtdparts - 定义与Linux兼容的MTD分区方案 |
* [http://www.denx.de/wiki/view/DULG/UBootCmdGroupExec Execution Control Commands] | * [http://www.denx.de/wiki/view/DULG/UBootCmdGroupExec Execution Control Commands] | ||
| − | ** source - | + | ** source - 从内存运行脚本 |
| − | ** bootm - | + | ** bootm - 从内存启动应用程序映像 |
| − | ** go - | + | ** go - 在地址‘addr’处启动应用程序 |
* [http://www.denx.de/wiki/view/DULG/UBootCmdGroupDownload Download Commands] | * [http://www.denx.de/wiki/view/DULG/UBootCmdGroupDownload Download Commands] | ||
| − | ** bootp - | + | ** bootp - 使用BOOTP / TFTP协议通过网络引导映像 |
| − | ** dhcp - | + | ** dhcp - 调用DHCP客户端以获得IP /启动参数 |
| − | ** loadb - | + | ** loadb - 通过串行线加载二进制文件(kermit模式) |
| − | ** loads - | + | ** loads - 通过串行线加载S-Record文件 |
| − | ** rarpboot- | + | ** rarpboot- 使用RARP/TFTP协议通过网络引导映像 |
| − | ** tftpboot- | + | ** tftpboot- 使用TFTP协议通过网络引导映像 |
* [http://www.denx.de/wiki/view/DULG/UBootCmdGroupEnvironment Environment Variables Commands] | * [http://www.denx.de/wiki/view/DULG/UBootCmdGroupEnvironment Environment Variables Commands] | ||
| − | ** printenv- | + | ** printenv- 打印环境变量 |
| − | ** saveenv - | + | ** saveenv - 将环境变量保存到永久存储 |
| − | ** setenv - | + | ** setenv - 设置环境变量 |
| − | ** run - | + | ** run - 在环境变量中运行命令 |
| − | ** bootd - | + | ** bootd - 启动默认设置,即运行‘bootcmd’ |
* [http://www.denx.de/wiki/view/DULG/UBootCmdFDT Flattened Device Tree support] | * [http://www.denx.de/wiki/view/DULG/UBootCmdFDT Flattened Device Tree support] | ||
| − | ** fdt addr - | + | ** fdt addr - 选择要处理的FDT |
| − | ** fdt list - | + | ** fdt list - 打印等级一级 |
| − | ** fdt print - | + | ** fdt print - 递归打印 |
| − | ** fdt mknode - | + | ** fdt mknode - 创建新节点 |
| − | ** fdt set - | + | ** fdt set - 设置节点属性 |
| − | ** fdt rm - | + | ** fdt rm - 删除节点或属性 |
| − | ** fdt move - | + | ** fdt move - 将FDT blob移动到新地址 |
| − | ** fdt chosen - | + | ** fdt chosen - 固定动态信息 |
* [http://www.denx.de/wiki/view/DULG/UBootCmdGroupSpecial Special Commands] | * [http://www.denx.de/wiki/view/DULG/UBootCmdGroupSpecial Special Commands] | ||
| − | ** i2c - | + | ** i2c - I2C子系统 |
* [http://www.denx.de/wiki/view/DULG/UBootStorageDevices Storage devices] | * [http://www.denx.de/wiki/view/DULG/UBootStorageDevices Storage devices] | ||
* [http://www.denx.de/wiki/view/DULG/UBootCmdGroupMisc Miscellaneous Commands] | * [http://www.denx.de/wiki/view/DULG/UBootCmdGroupMisc Miscellaneous Commands] | ||
| − | ** echo - | + | ** echo - 将参数返回到控制台 |
| − | ** reset - | + | ** reset - 执行CPU重置 |
| − | ** sleep - | + | ** sleep - 将执行延迟预定义的时间 |
| − | ** version - | + | ** version - 打印监视器版本 |
| − | + | 要添加新命令,请参阅{{CodeSource | U-Boot | doc/README.commands }}. | |
| − | |||
=== U-Boot environment variables === | === U-Boot environment variables === | ||
| − | + | U-Boot行为是通过环境变量配置的。 | |
| − | + | 环境变量请参阅[http://www.denx.de/wiki/view/DULG/UBootEnvVariables Manual] 和{{CodeSource | U-Boot | README | README}} 。 | |
On the first boot, U-Boot uses a default environment embedded in the U-Boot binary. You can modify it by changing the content of CONFIG_EXTRA_ENV_SETTINGS in your configuration file (for example ./include/configs/stm32mp1.h) (see {{CodeSource | U-Boot | README | README}} / - Default Environment). | On the first boot, U-Boot uses a default environment embedded in the U-Boot binary. You can modify it by changing the content of CONFIG_EXTRA_ENV_SETTINGS in your configuration file (for example ./include/configs/stm32mp1.h) (see {{CodeSource | U-Boot | README | README}} / - Default Environment). | ||
2020年11月3日 (二) 10:03的版本
目录
Das U-Boot
Das U-Boot (“通用引导加载程序”或U-Boot) 是一种开源引导加载程序,可用于ST板上以初始化平台并加载Linux® 内核。
- 官方网站: https://www.denx.de/wiki/U-Boot
- 官方手册: project documentation 和 https://www.denx.de/wiki/DULG/Manual
- 官方的源代码 可在 git 存储库下找到[1]
PC $> git clone https://gitlab.denx.de/u-boot/u-boot.git
在开始使用U-Boot之前,请阅读README | |}} README file 。它涵盖以下主题:
- 源文件树结构
- 配置定义说明
- 关于构建U-Boot的说明
- Hush外壳的简要说明
- 常用环境变量列表
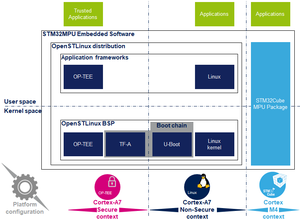
U-Boot overview
同一个U-Boot源可以生成SPL和U-Boot中使用的两个固件 STM32 MPU boot chain:
- 受信任的引导链:TF-A作为FSBL,U-Boot作为SSBL
- 基本启动链:SPL作为FSBL,U-Boot作为SSBL
| 基本启动链不能用于产品开发 (请参见Boot chains overview 以获取详细信息). |
它仅作为最简单的SSBL的示例提供,并支持上游U-Boot开发。但是,当SPL与U-Boot中提供的用于基本引导链的最小安全监视器结合使用时,已经发现了几个已知的限制。它们适用于:
- 功率
- 安全访问寄存器
- 有限的功能(STM32CubeProgrammer / boot from NAND Flash memory).
没有针对这些限制的修复计划。
SPL: FSBL for basic boot
U-Boot SPL 或 SPL 是 the basic boot chain的第一阶段引导加载程序(FSBL)。
它是从U-Boot源生成的小二进制文件(引导实用程序),并存储在内部有限大小的嵌入式RAM中。SPL的主要功能如下:
- 它由ROM代码加载。
- 它执行初始的CPU和板配置(时钟和DDR内存)。
- 它将SSBL(U-Boot)加载到DDR内存中。
U-Boot: SSBL
U-Boot 是STM32 MPU平台的默认第二阶段引导程序(SSBL)。它同时用于 trusted and basic引导链
SSBL的主要功能如下:
- 它是可配置和消耗的。
- 它具有一个简单的命令行界面(CLI),允许用户通过串行端口控制台进行交互。
- 它提供脚本功能
- 它将内核加载到RAM中并控制内核
- 它管理多个内部和外部设备,例如NAND和NOR闪存,以太网和USB。
- 它支持以下功能和命令:
- 文件系统:FAT, UBI/UBIFS, JFFS
- IP堆栈:FTP
- 显示: LCD, HDMI, BMP for splashcreen
- USB: host (mass storage) or device (DFU stack)
SPL phases
SPL 在SYSRAM中执行以下主要阶段:
- board_init_f(): 驱动程序初始化,包括DDR初始化(最小堆栈和堆:CONFIG_SPL_STACK_R_MALLOC_SIMPLE_LEN)
- DDR内存中堆的配置(CONFIG_SPL_SYS_MALLOC_F_LEN)
- board_init_r(): 初始化在SPL设备树中激活的其他驱动程序
- 加载并执行U-Boot(或Falcon模式下的内核[1]: doc/README.falcon | |}} README.falcon ).
U-Boot phases
U-Boot 在DDR内存中执行以下主要阶段:
- Pre-relocation 初始化 (common/board_f.c): 在CONFIG_SYS_TEXT_BASE加载地址上运行的最小初始化(例如CPU,时钟,重置,DDR和控制台)
- Relocation: 将代码复制到DDR内存的末尾。
- Post-relocation initialization:(common/board_r.c): 初始化所有驱动程序。
-
Command execution 通过自动引导(CONFIG_AUTOBOOT)或控制台shell
- 启动命令的执行(默认情况下 bootcmd=CONFIG_BOOTCOMMAND):
例如,将命令bootm执行到:- 加载并检查映像(例如内核,设备树和ramdisk)
- 修复内核设备树
- 安装安全监视器(可选)或
- 将控制权传递给Linux内核(或另一个目标应用程序)
- 启动命令的执行(默认情况下 bootcmd=CONFIG_BOOTCOMMAND):
U-Boot configuration
U-Boot二进制配置基于
-
Kbuild infrastructure (与Linux Kernel, 您可以在U-Boot中使用
make menuconfig)
配置基于以下各项:- 在 Kconfig 文件中定义的选项(CONFIG _ compilation 标志)
- 所选配置文件:configs/ | |}} configs/stm32mp*_defconfig
-
other compilation flags 定义于include/configs/ | |}} include/configs/stm32mp*.h (这些标志将逐步迁移到Kconfig)
文件名通过CONFIG_SYS_CONFIG_NAME配置。
对于 {{#vardefine:info|}}{{#vardefine:dev|MP15x lines}}{{#vardefine:info| }}STM32{{#var:dev}}{{#var:info}}, 使用了include/configs/stm32mp1.h | |}} include/configs/stm32mp1.h 文件。
}}STM32{{#var:dev}}{{#var:info}}, 使用了include/configs/stm32mp1.h | |}} include/configs/stm32mp1.h 文件。
- DeviceTree: U-Boot和SPL二进制文件包括在运行时解析的设备树blob
所有的配置标志(前缀为 CONFIG_)都在源代码中描述, 或者在 README | |}} README 文件中,或者在doc/ | |}} documentation directory 目录中。
例如,CONFIG_SPL激活SPL编译
因此,为了选择一个预定义的配置,需要为主板编译 U-Boot,select the <target> 和 the device tree 。
有关示例,请参阅#U-Boot_build。
Kbuild
与内核一样,U-Boot构建系统也基于 configuration symbols (在Kconfig文件中定义). 选定的值存储在build目录的.config文件中,具有相同的Makefile目标。
按照以下步骤进行:
- 选择预定义的配置(configs/ | |}} configs directory 中的defconfig文件) 并生成第一个 .config:
PC $> make <config>_defconfig.
- 使用以下五个
make命令之一更改U-Boot编译配置(修改.config):
PC $> make menuconfig --> menu based program PC $> make config --> line-oriented configuration PC $> make xconfig --> QT program[2] PC $> make gconfig --> GTK program PC $> make nconfig --> ncurse menu based program
然后,您可以使用更新的.config编译U-Boot。
Warning: 修改是在构建目录的本地执行的。在 make distclean 之后它将丢失.
保存您的配置以将其用作defconfig文件:
PC $> make savedefconfig
此目标将当前配置保存为build目录中的defconfig文件。 然后可以将其与预定义的配置进行比较(configs/stm32mp*defconfig).
其他makefile目标如下:
PC $> make help
....
Configuration targets:
config - Update current config utilising a line-oriented program
nconfig - Update current config utilising a ncurses menu based
program
menuconfig - Update current config utilising a menu based program
xconfig - Update current config utilising a Qt based front-end
gconfig - Update current config utilising a GTK+ based front-end
oldconfig - Update current config utilising a provided .config as base
localmodconfig - Update current config disabling modules not loaded
localyesconfig - Update current config converting local mods to core
defconfig - New config with default from ARCH supplied defconfig
savedefconfig - Save current config as ./defconfig (minimal config)
allnoconfig - New config where all options are answered with no
allyesconfig - New config where all options are accepted with yes
allmodconfig - New config selecting modules when possible
alldefconfig - New config with all symbols set to default
randconfig - New config with random answer to all options
listnewconfig - List new options
olddefconfig - Same as oldconfig but sets new symbols to their
default value without prompting
Device tree
请参阅doc/README.fdt-control | |}} doc/README.fdt-control 以获取详细信息。
板设备树具有与内核相同的绑定。它集成在SPL和U-Boot二进制文件中:
- 默认情况下,它被附加在代码的末尾(CONFIG_OF_SEPARATE).
- 它嵌入在U-Boot二进制文件(CONFIG_OF_EMBED)中。这对调试很有用,因为它可以轻松加载.elf文件。
defconfig文件中有一个默认的设备树(通过设置CONFIG_DEFAULT_DEVICE_TREE)。
您可以使用DEVICE_TREE make标志选择另一个受支持的设备树。 对于stm32mp板,相应的文件为: arch/arm/dts/ | |}} arch/arm/dts/stm32mp*.dts .
PC $> make DEVICE_TREE=<dts-file-name>
或提供预编译的设备树blob(using EXT_DTB option):
PC $> make EXT_DTB=boot/<dts-file-name>.dtb
SPL设备树也从该设备树生成。 但是为了减小其大小,U-Boot生成文件使用fdtgrep工具来解析完整的U-Boot DTB并识别SPL所需的所有驱动程序。
为此,U-Boot使用特定的设备树标志来定义相关的驱动程序是否在U-Boot重定位之前初始化和/或相关的节点是否存在于SPL中:
- u-boot,dm-pre-reloc => 存在于SPL中,在U-Boot中重新定位之前初始化
- u-boot,dm-pre-proper => 在U-Boot中重新定位之前初始化
- u-boot,dm-spl => 存在于SPL中
在U-Boot使用的设备树中,这些标志需要添加到SPL或U-Boot中使用的每个节点中,然后再进行重定位以及每个使用的句柄(时钟,复位,引脚控制)。
U-Boot command line interface (CLI)
请参阅 U-Boot Command Line Interface.
如果CONFIG_AUTOBOOT已激活,则在显示以下行并执行bootcmd(CONFIG_BOOTCOMMAND)后,您有CONFIG_BOOTDELAY秒(默认情况下为2秒)通过按任意键进入控制台:
Hit any key to stop autoboot: 2
Commands
这些命令在cmd/ | |}} cmd/*.c . 通过相应的 CONFIG_CMD_* 配置标志激活它们。
使用U-Boot shell中的help 命令列出设备上可用的命令:
Board $> help
以下是从中提取的所有命令的列表 U-Boot Manual (不详尽):
-
Information Commands
- bdinfo - 打印板信息结构
- coninfo - 打印控制台设备和信息
- flinfo - 打印闪存信息
- iminfo - 打印应用程序映像的标题信息
- help - 打印在线帮助
-
Memory Commands
- base - 打印或设置地址偏移量
- crc32 - 校验和计算
- cmp - 内存比较
- cp - 内存拷贝
- md - 内存显示
- mm - 内存修改(自动递增)
- mtest - 简单的RAM测试
- mw - 内存写入(填充)
- nm - 内存修改(常量地址)
- loop - 地址范围内无限循环
-
Flash Memory Commands
- cp - 内存复制
- flinfo - 打印闪存信息
- erase - 清除闪存
- protect - 启用或禁用闪存写入保护
- mtdparts - 定义与Linux兼容的MTD分区方案
-
Execution Control Commands
- source - 从内存运行脚本
- bootm - 从内存启动应用程序映像
- go - 在地址‘addr’处启动应用程序
-
Download Commands
- bootp - 使用BOOTP / TFTP协议通过网络引导映像
- dhcp - 调用DHCP客户端以获得IP /启动参数
- loadb - 通过串行线加载二进制文件(kermit模式)
- loads - 通过串行线加载S-Record文件
- rarpboot- 使用RARP/TFTP协议通过网络引导映像
- tftpboot- 使用TFTP协议通过网络引导映像
-
Environment Variables Commands
- printenv- 打印环境变量
- saveenv - 将环境变量保存到永久存储
- setenv - 设置环境变量
- run - 在环境变量中运行命令
- bootd - 启动默认设置,即运行‘bootcmd’
-
Flattened Device Tree support
- fdt addr - 选择要处理的FDT
- fdt list - 打印等级一级
- fdt print - 递归打印
- fdt mknode - 创建新节点
- fdt set - 设置节点属性
- fdt rm - 删除节点或属性
- fdt move - 将FDT blob移动到新地址
- fdt chosen - 固定动态信息
-
Special Commands
- i2c - I2C子系统
- Storage devices
-
Miscellaneous Commands
- echo - 将参数返回到控制台
- reset - 执行CPU重置
- sleep - 将执行延迟预定义的时间
- version - 打印监视器版本
要添加新命令,请参阅doc/README.commands | |}} doc/README.commands .
U-Boot environment variables
U-Boot行为是通过环境变量配置的。
环境变量请参阅Manual 和README | |}} README 。
On the first boot, U-Boot uses a default environment embedded in the U-Boot binary. You can modify it by changing the content of CONFIG_EXTRA_ENV_SETTINGS in your configuration file (for example ./include/configs/stm32mp1.h) (see README | |}} README / - Default Environment).
This environment can be modified and saved in the boot device. When it is present, it is loaded during U-Boot initialization:
- for e•MMC/SD card boot (CONFIG_ENV_IS_IN_EXT4), in the bootable ext4 partition "bootfs" in
in file CONFIG_ENV_EXT4_FILE="uboot.env". - for NAND boot (CONFIG_ENV_IS_IN_UBI), in the two UBI volumes "config" (CONFIG_ENV_UBI_VOLUME) and "config_r" (CONFIG_ENV_UBI_VOLUME_REDUND).
- for NOR boot (CONFIG_ENV_IS_IN_SPI_FLASH), in the u-boot_env mtd parttion (at offset CONFIG_ENV_OFFSET).
env command
The env command allows displaying, modifying and saving the environment in U-Boot console.
Board $> help env env - environment handling commands Usage: env default [-f] -a - [forcibly] reset default environment env default [-f] var [...] - [forcibly] reset variable(s) to their default values env delete [-f] var [...] - [forcibly] delete variable(s) env edit name - edit environment variable env exists name - tests for existence of variable env print [-a | name ...] - print environment env print -e [name ...] - print UEFI environment env run var [...] - run commands in an environment variable env save - save environment env set -e name [arg ...] - set UEFI variable; unset if 'arg' not specified env set [-f] name [arg ...]
Example: proceed as follows to restore the default environment and save it. This is useful after a U-Boot upgrade:
Board $> env default -a Board $> env save
bootcmd
"bootcmd" variable is the autoboot command. It defines the command executed when U-Boot starts (CONFIG_BOOTCOMMAND).
For stm32mp, CONFIG_BOOTCOMMAND="run bootcmd_stm32mp":
Board $> env print bootcmd bootcmd=run bootcmd_stm32mp
"bootcmd_stm32mp" is a script that selects the command to be executed for each boot device (see ./include/configs/stm32mp1.h), based on generic distro scripts:
- for serial/usb: execute the
stm32progcommand. - for mmc boot (e•MMC, SD card), boot only on the same device (bootcmd_mmc...).
- for nand boot, boot with on ubifs partition on nand (bootcmd_ubi0).
- for nor boot, use the default order e•MMC (SDMMC 1)/ NAND / SD card (SDMMC 0) / SDMMC2 (the default bootcmd: distro_bootcmd).
Board $> env print bootcmd_stm32mp
You can then change this configuration:
- either permanently in your board file (default environment by CONFIG_EXTRA_ENV_SETTINGS or change CONFIG_BOOTCOMMAND value) or
- temporarily in the saved environment:
Board $> env set bootcmd run bootcmd_mmc0 Board $> env save
Note: To reset the environment to its default value:
Board $> env default bootcmd Board $> env save
Generic Distro configuration
Refer to doc/README.distro | |}} doc/README.distro for details.
This feature is activated by default on ST boards (CONFIG_DISTRO_DEFAULTS):
- one boot command (bootmcd_xxx) exists for each bootable device.
- U-Boot is independent of the Linux distribution used.
- bootcmd is defined in ./include/config_distro_bootcmd.h | |}} ./include/config_distro_bootcmd.h
When DISTRO is enabled, the command that is executed by default is include/config_distro_bootcmd.h| |}} include/config_distro_bootcmd.h :
bootcmd=run distro_bootcmd
This script tries any device found in the 'boot_targets' variable and executes the associated bootcmd.
Example for mmc0, mmc1, mmc2, pxe and ubifs devices:
bootcmd_mmc0=setenv devnum 0; run mmc_boot bootcmd_mmc1=setenv devnum 1; run mmc_boot bootcmd_mmc2=setenv devnum 2; run mmc_boot bootcmd_pxe=run boot_net_usb_start; dhcp; if pxe get; then pxe boot; fi bootcmd_ubifs0=setenv devnum 0; run ubifs_boot
U-Boot searches for a extlinux.conf configuration file for each bootable device. This file defines the kernel configuration to be used:
- bootargs
- kernel + device tree + ramdisk files (optional)
- FIT image
U-Boot scripting capabilities
"Script files" are command sequences that are executed by the U-Boot command interpreter. This feature is particularly useful to configure U-Boot to use a real shell (hush) as command interpreter.
See U-Boot script manual for an example.
U-Boot build
Prerequisites
- a PC with Linux and tools:
- U-Boot source code
PC $> git clone https://github.com/STMicroelectronics/u-boot
- from the Mainline U-Boot in official GIT repository [4]
PC $> git clone https://gitlab.denx.de/u-boot/u-boot.git
ARM cross compiler
A cross compiler [5] must be installed on your Host (X86_64, i686, ...) for the ARM targeted Device architecture. In addition, the $PATH and $CROSS_COMPILE environment variables must be configured in your shell.
You can use gcc for ARM, available in:
- the SDK toolchain (see Cross-compile with OpenSTLinux SDK)
PATH and CROSS_COMPILE are automatically updated. - an existing package
For example, install gcc-arm-linux-gnueabihf on Ubuntu/Debian: (PC $> sudo apt-get. - an existing toolchain:
- latest gcc toolchain provided by arm (https://developer.arm.com/open-source/gnu-toolchain/gnu-a/downloads/)
- gcc v7 toolchain provided by linaro: (https://www.linaro.org/downloads/)
For example, to use gcc-arm-9.2-2019.12-x86_64-arm-none-linux-gnueabihf.tar.xz from arm, extract the toolchain in $HOME and update your environment with:
PC $> export PATH=$HOME/gcc-arm-9.2-2019.12-x86_64-arm-none-linux-gnueabihf/bin:$PATH PC $> export CROSS_COMPILE=arm-none-linux-gnueabihf-
For example, to use gcc-linaro-7.2.1-2017.11-x86_64_arm-linux-gnueabi.tar.xz
from https://releases.linaro.org/components/toolchain/binaries/7.2-2017.11/arm-linux-gnueabi/
Unzip the toolchain in $HOME and update your environment with:
PC $> export PATH=$HOME/gcc-linaro-7.2.1-2017.11-x86_64_arm-linux-gnueabi/bin:$PATH PC $> export CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabi-
Compilation
In the U-Boot source directory, select the <target> and the <device tree> for your configuration and then execute the make all command:
PC $> make <target>_defconfig PC $> make DEVICE_TREE=<device-tree> all
Optionally KBUILD_OUTPUT can be used to change the output directory to compile several targets or not to compile in the source directory. For example:
PC $> export KBUILD_OUTPUT=../build/basic
DEVICE_TREE can also be exported to your environment when only one board is supported. For example:
PC $> export DEVICE_TREE=stm32mp157c-ev1
Examples from STM32MP15 U-Boot:
Three configurations are supported for {{#vardefine:info|}}{{#vardefine:dev|MP15x lines}}{{#vardefine:info| ![]() }}STM32{{#var:dev}}{{#var:info}}:
}}STM32{{#var:dev}}{{#var:info}}:
- stm32mp15_trusted_defconfig: trusted boot chain, U-Boot (without SPL) is unsecure and uses Secure monitor from TF-A
- stm32mp15_optee_defconfig: trusted boot chain, U-Boot (without SPL) is unsecure and uses Secure monitor from SecureOS = OP-TEE
- stm32mp15_basic_defconfig: basic boot chain, with an SPL as FSBL, U-BOOT is secure and installs monitor with PSCI
The board diversity is only managed with the device tree.
PC $> export KBUILD_OUTPUT=../build/trusted PC $> make stm32mp15_trusted_defconfig PC $> make DEVICE_TREE=stm32mp157c-<board> all
PC $> export KBUILD_OUTPUT=../build/optee PC $> export DEVICE_TREE=stm32mp157c-<board> PC $> make stm32mp15_optee_defconfig PC $> make all
PC $> make stm32mp15_basic_defconfig PC $> make DEVICE_TREE=stm32mp157c-<board> all
Use help to list other targets:
PC $> make help
Output files
The resulting U-Boot files are located in your build directory (U-Boot or KBUILD_OUTPUT).
Two binary formats are used for stm32mp devices:
- STM32 image format (*.stm32), managed by mkimage U-Boot tools and Signing_tool. It is requested by ROM code and TF-A (see STM32 header for binary files for details).
- uImage (*.img) format, file including a U-Boot header, managed by SPL and U-Boot (for kernel load)
The U-Boot generated files are the following
- For Trusted boot chain (TF-A is used as FSBL, with or without OP-TEE)
- u-boot.stm32 : U-Boot binary with STM32 image header, loaded by TF-A
- For Basic boot chain (SPL is used as FSBL)
- u-boot-spl.stm32 : SPL binary with STM32 image header, loaded by ROM code
- u-boot.img : U-Boot binary with uImage header, loaded by SPL
The files used to debug with gdb are
- u-boot : elf file for U-Boot
- spl/u-boot-spl : elf file for SPL
References
- ↑ https://www.denx.de/wiki/pub/U-Boot/MiniSummitELCE2013/2013-ELCE-U-Boot-Falcon-Boot.pdf
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Xconfig
- ↑ https://github.com/STMicroelectronics/u-boot
- ↑ https://gitlab.denx.de/u-boot/u-boot.git or https://github.com/u-boot/u-boot
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cross_compiler
<securetransclude src="ProtectedTemplate:PublicationRequestId" params="12893 | 2019-08-01 |"></securetransclude>